Rangkuman Before UTS
Linked List
Linked List Definition
A linked list is a dynamic data structure where a node is made up of two items - the data and a reference (or pointer) which points to the next node. A linked list is a collection of nodes where each node is connected to the next node through a pointer. The first node is called a head and if the list is empty then the value of head is NULL.For a real-world analogy of linked list, you can think of conga line, a special kind of dance in which people line up behind each other with hands on shoulders of the person in front.
 |
Circular Single Linked list
In Circular Single Linked List, last node contains a pointer to the first node,We can have a circular singly linked list as well as a circular doubly linked list.There is no storing of NULL values in the listImplementation
Insertion
A node can be added in three ways:
A node can be added in three ways:
- Insertion in an empty list
- Insertion at the beginning of the list
- Insertion at the end of the list
- Insertion in between the nodes
Doubly Linked List
A linked list data structure with two link, one that contain reference to the next data and one that contain reference to the previous data.
Example:

struct tnode {
int value;
struct tnode *next;
struct tnode *prev;
};
•
struct tnode *head = 0;
struct tnode *tail = 0;
Implementation:
Insert:
Insert new node behind the tail:
struct tnode *node =
(struct tnode*) malloc(sizeof(struct tnode));
node->value = x;
node->next = NULL;
node->prev = tail;
tail->next = node;
tail = node;
Insert new node in any location between head and tail:
struct tnode *a = ??;
struct tnode *b = ??;
// the new node will be inserted between a and b
struct tnode *node =
(struct tnode*) malloc(sizeof(struct tnode));
node->value = x;
node->next = b;
node->prev = a;
a->next = node;
b->prev = node;
Delete:
There are 4 conditions we should pay attention when deleting:
The node to be deleted is the only node in linked list.
The node to be deleted is head.
The node to be deleted is tail.
The node to be deleted is not head or tail.
•If the node to be deleted is the only node:
free(head);
head = NULL;
tail = NULL;
•If the node to be deleted is head:
head = head->next;
free(head->prev);
head->prev = NULL;
•If the node to be deleted is tail:
tail = tail->prev;
free(tail->next);
tail->next = NULL;
•If the node to be deleted is not in head or tail:
struct tnode *curr = head;
while ( curr->next->value != x ) curr = curr->next;
struct tnode *a = curr;
struct tnode *del = curr->next;
struct tnode *b = curr->next->next;
a->next = b;
b->prev = a;
free(del);
Circular Doubly Linked List
Circular Doubly Linked List has properties of both doubly linked list and circular linked list in which two consecutive elements are linked or connected by previous and next pointer and the last node points to first node by next pointer and also the first node points to last node by previous pointer.
Hash And Binary
Hashing
Hash Table
Hash table is a data structure that implements an associative array abstract data type, a structure that can map keys to values. A hash table uses a hash function to compute an index, also called a hash code, into an array of buckets or slots, from which the desired value can be found.
Example:
Supposed we want to store 5 string: define, float, exp, char, atan into a hash table with size 26. The hash function we will use is “transform the first character of each string into a number between 0..25”
(a will be 0, b will be 1, c will be 2, …, z will be 25).
There are many ways to hash a string into a key. The following are some of the important methods for constructing hash functions.
•Mid-square
Mid-Square hashing is a hashing technique in which unique keys are generated. In this technique, a seed value is taken and it is squared. Then, some digits from the middle are extracted. These extracted digits form a number which is taken as the new seed. This technique can generate keys with high randomness if a big enough seed value is taken.
Hash Function
Example:
Suppose a 4-digit seed is taken. seed = 4765
Hence, square of seed is = 4765 * 4765 = 22705225
Now, from this 8-digit number, any four digits are extracted (Say, the middle four).
So, the new seed value becomes seed = 7052
Now, square of this new seed is = 7052 * 7052 = 49730704
Again, the same set of 4-digits is extracted.
So, the new seed value becomes seed = 7307
Hence, square of seed is = 4765 * 4765 = 22705225
Now, from this 8-digit number, any four digits are extracted (Say, the middle four).
So, the new seed value becomes seed = 7052
Now, square of this new seed is = 7052 * 7052 = 49730704
Again, the same set of 4-digits is extracted.
So, the new seed value becomes seed = 7307
•Division (most common)
Divide the string/identifier by using the modulus operator.
Example:
"COBB” would be stored at the location ( 64+3 + 64+15 + 64+2 + 64+2) % 97 = 88
•Rotating Hash
Example:
–Given hash address = 56890
–Rotation result: 09865(fold the digits)
Linear probing has a bad search complexity if there are many collisions.
•Folding
Partition the string/identifier into several parts, then add the parts together to obtain the hash key
Example:
Key:4578
Parts: 45 and 78
Sum:123
Hash Value:23
•Digit Extraction
A predefined digit of the given number is considered as the hash address.
Example:
X=15,678
Hash Code=168
•Rotating Hash
Use any hash method (such as division or mid-square method)
After getting the hash code/address from the hash method, do rotation
Rotation is performed by shifting the digits to get a new hash address
After getting the hash code/address from the hash method, do rotation
Rotation is performed by shifting the digits to get a new hash address
–Given hash address = 56890
–Rotation result: 09865(fold the digits)
Collision
The situation where there are several srings use the same hash key
Two general ways to handle this problem:
-Linear Probing:
Search the next empty slot and put the string there.
-Chaining:
Put the string in a slot as a chained list (linked list).
In chaining, we store each string in a chain (linked list). So if there is collision, we onlyneed to iterate on that chain.
Tree
Tree is a non linear data structures that represents the hierarchical relationships among the data object .The node in the tree need no to be stored contiguously and can be stored anywhere and linked by pointers.
Tree Concept
-Tree is a collection of one or more nodes
-Node at the top is called a root
-A line connecting the parent to the child is edge.-Nodes that do not have children are called leaf.
-Nodes that have the same parent are called sibling.
-Degree of node is the total sub tree of the node.
-Height/Depth is the maximum degree of nodes in a tree.
-If there is a line that connects a to b, then a is called the ancestor of b, and b is a descendant of a.
Binary Tree Concept
Binary tree is a rooted tree that contain maximum of two children(left child and right child)
Type Of Binary Tree
-Perfect Binary Tree is a binary tree in which all interior nodes have two children and all leaves have the same depth or same level.
-Complete Binary Tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible. A perfect binary tree is a complete binary tree.
-Skewed Binary Tree is a binary tree in which each node has at most one child.
-Balance Binary Tree is a binary tree structure in which the left and right subtrees of every node differ in height by no more than 1.[One may also consider binary trees where no leaf is much farther away from the root than any other leaf.
Threaded Binary Tree Concept
-Threaded Binary Tree is same as the binary tree,the difference between them is in storing of NULL pointers
-In the linked representation, a number of nodes contain a NULL pointer either in their left or right fields or in both.
-This space that is wasted in storing a NULL pointer can be efficiently used to store some other useful peace of information
-TOP which is used to store the address of the topmost element of the stack.
-MAX which is used to store the maximum number of elements that the stack can hold.
–One that stores the data
–Another that stores the address of the next element
•The START pointer of the linked list is used as the FRONT
•All insertions will be done at the REAR, and all the deletions are done at the FRONT end.
•If FRONT = REAR = NULL, then it indicates that the queue is empty
•pop() : remove an item from the front of the queue.
•front() : reveal/return the most front item from the queue.
•If R reach MAXN then set R as zero, do the same to L.
•It is also known as circular queue.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/mid-square-hashing/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_tree
Stack And Queue
Stack
Stack is a basic data structure that can be logically thought of as a linear structure represented by a real physical stack or pile, a structure where insertion and deletion of items takes place at one end called top of the stack.
The basic implementation of a stack is also called a LIFO (Last In First Out) to demonstrate the way it accesses data, since as we will see there are various variations of stack implementations.
There are basically three operations that can be performed on stacks. They are inserting an item into a stack (push), deleting an item from the stack, and displaying the contents of the stack.
Array Representation
•Stack has two variables:-TOP which is used to store the address of the topmost element of the stack.
-MAX which is used to store the maximum number of elements that the stack can hold.
-If TOP = NULL, then indicates that the stack is empty.
-If TOP = MAX – 1, then the stack is full.
•pop() : remove an item from the top of the stack.
•top() : reveal/return the top item from the stack.
-If TOP = MAX – 1, then the stack is full.
Linked List Representation
A stack can be represented by using nodes of the linked list.
Each node contains two fields : data(info) and next(link)
The data field of each node contains an item in the stack and the corresponding next field points to the node containing the next item in the stack
The top refers to the top most node (The last item inserted) in the stack.
The empty stack is represented by setting top to nut. Because the way the nodes are pointing, push and pop operations are easy to accomplish.
Stack Operation
•push(x) : add an item x to the top of the stack.•pop() : remove an item from the top of the stack.
•top() : reveal/return the top item from the stack.
Infix, Postfix, Prefix
•Prefix : operator is written before operands
Example:+7 * 4 5 = 27
•Infix : operator is written between operands
Example:7 + 4 * 5 = 27
•Postfix : operator is written after operands
•Postfix : operator is written after operands
Example:7 4 5 * + = 27
Infix Notation
Infix Notation
Evaluate a given infix expression: 4 + 6 * (5 – 2) / 3.
To evaluate infix notation, we should search the highest precedence operator in the string.
4 + 6 * (5 – 2) / 3 search the highest precedence operator, it is ( )
4 + 6 * 3 / 3 search the highest precedence operator, it is *
4 + 18 / 3 search the highest precedence operator, it is /
4 + 6 search the highest precedence operator, it is +
10
Postfix Notation
To evaluate infix notation, we should search the highest precedence operator in the string.
4 + 6 * (5 – 2) / 3 search the highest precedence operator, it is ( )
4 + 6 * 3 / 3 search the highest precedence operator, it is *
4 + 18 / 3 search the highest precedence operator, it is /
4 + 6 search the highest precedence operator, it is +
10
Postfix Notation
Using Stack
Evaluating a postfix notation can be done in O(N), which is faster than O(N2)
Algorithm:
Scan the string from left to right, for each character in the string:
•If it is an operand, push it into stack.
•If it is an operator, pop twice (store in variable A and B respectively) and push(B operator A).
Pay attention here! It is (B operator A), not (A operator B).
The result will be stored in the only element in stack.
Evaluating a prefix notation is similar to postfix notation,the string is scanned from right to left.
Conversion Infix To Postfix
Evaluating a postfix notation can be done in O(N), which is faster than O(N2)
Algorithm:
Scan the string from left to right, for each character in the string:
•If it is an operand, push it into stack.
•If it is an operator, pop twice (store in variable A and B respectively) and push(B operator A).
Pay attention here! It is (B operator A), not (A operator B).
The result will be stored in the only element in stack.
Prefix Notation
Using StackEvaluating a prefix notation is similar to postfix notation,the string is scanned from right to left.
Conversion Infix To Postfix
Manually
Algorithm:
1.Search for the operator which has the highest precedence
2.Put that operator behind the operands
3.Repeat until finish
•Manually
•A + B – C x D ^ E / F , power has the highest precedence
•A + B – C x D E ^ / F , put ^ behind D and E
•A + B – C x D E ^ / F , x and / have same level precedence
•A + B – C D E ^ x / F , put x at the end
•A + B – C D E ^ x / F , continue with the same algorithm till finish
•A + B – C D E ^ x F /
•A + B – C D E ^ x F /
•A B + – C D E ^ x F /
•A B + – C D E ^ x F /
•A B + C D E ^ x F / – , this is the Postfix notation
Conversion Infix To Prefix
Manually
Algorithm:
1.Search for the operator which has the highest precedence
2.Put that operator before the operands
3.Repeat until finish
Manually
A + B – C x D ^ E / F
A + B – C x ^ D E / F
A + B – C x ^ D E / F
A + B – x C ^ D E / F
A + B – x C ^ D E / F
A + B – / x C ^ D E F
A + B – / x C ^ D E F
+ A B – / x C ^ D E F
+ A B – / x C ^ D E F
– + A B / x C ^ D E F , this is the Prefix notation
Algorithm:
1.Search for the operator which has the highest precedence
2.Put that operator behind the operands
3.Repeat until finish
•Manually
•A + B – C x D ^ E / F , power has the highest precedence
•A + B – C x D E ^ / F , put ^ behind D and E
•A + B – C x D E ^ / F , x and / have same level precedence
•A + B – C D E ^ x / F , put x at the end
•A + B – C D E ^ x / F , continue with the same algorithm till finish
•A + B – C D E ^ x F /
•A + B – C D E ^ x F /
•A B + – C D E ^ x F /
•A B + – C D E ^ x F /
•A B + C D E ^ x F / – , this is the Postfix notation
Conversion Infix To Prefix
Manually
Algorithm:
1.Search for the operator which has the highest precedence
2.Put that operator before the operands
3.Repeat until finish
Manually
A + B – C x D ^ E / F
A + B – C x ^ D E / F
A + B – C x ^ D E / F
A + B – x C ^ D E / F
A + B – x C ^ D E / F
A + B – / x C ^ D E F
A + B – / x C ^ D E F
+ A B – / x C ^ D E F
+ A B – / x C ^ D E F
– + A B / x C ^ D E F , this is the Prefix notation
Depth First Search
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. The algorithm starts at the root node (selecting some arbitrary node as the root node in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
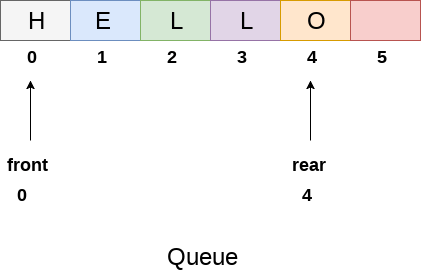
Queue
•Queue is an important data structure which stores its elements in an ordered manner.
•Queue can be implemented by either using arrays or linked lists.
•The elements in a queue are added at one end called the rear and removed from the other one end called front.
•The data are stored in First In First Out (FIFO) way, this is the main difference between stack and queue.
•The elements in a queue are added at one end called the rear and removed from the other one end called front.
•The data are stored in First In First Out (FIFO) way, this is the main difference between stack and queue.
Array Representation

Linked List Representation
•In a linked queue, every element has two parts–One that stores the data
–Another that stores the address of the next element
•The START pointer of the linked list is used as the FRONT
•All insertions will be done at the REAR, and all the deletions are done at the FRONT end.
•If FRONT = REAR = NULL, then it indicates that the queue is empty
Queue Operation
•push(x) : add an item x to the back of the queue.•pop() : remove an item from the front of the queue.
•front() : reveal/return the most front item from the queue.
Circular Queue
•We can wrap-around index L and R.•If R reach MAXN then set R as zero, do the same to L.
•It is also known as circular queue.
Queue Applications
•Deques
is a list in which elements can be inserted or deleted at either end. It is also known as a head-tail linked list, because elements can be added to or removed from the front (head) or back (tail).
•Priority Queues
A priority queue is an abstract data type in which the each element is assigned a priority.
The general rule of processing elements of a priority queue can be given as:
•An element with higher priority is processes before an element with lower priority
•Two elements with same priority are processed on a first come first served (FCFS) basis
The general rule of processing elements of a priority queue can be given as:
•An element with higher priority is processes before an element with lower priority
•Two elements with same priority are processed on a first come first served (FCFS) basis
•Breadth First Search
Breadth First Search (BFS) like DFS is also an algorithm for traversing or searching in a tree or graph. We start at the root of the tree (or some arbitrary node in graph) and explore all neighboring nodes level per level until we find the goal.
Binary search tree (BST), also known as sorted binary tree, is a node-based data structure in which each node has no more than two child nodes. Each child must either be a leaf node or the root of another binary search tree. The left sub-tree contains only nodes with keys less than the parent node; the right sub-tree contains only nodes with keys greater than the parent node.The BST data structure is the basis for a number of highly efficient sorting and searching algorithms, and it can be used to construct more abstract data structures including sets, multisets, and associative arrays.
For a node x in of a BST T,
–the left subtree of x contains elements that are smaller than those stored in x,
–the right subtree of x contains all elements that are greater than those stored in x,
Binary Search Tree Operations
Search() : find key in the BST
Insert() : insert new key into BST
Remove() : remove key from BST
Binary Search Tree
Definition
BST Rules
–the left subtree of x contains elements that are smaller than those stored in x,
–the right subtree of x contains all elements that are greater than those stored in x,
Binary Search Tree Operations
Search() : find key in the BST
Whenever an element is to be searched, start searching from the root node. Then if the data is less than the key value, search for the element in the left subtree. Otherwise, search for the element in the right subtree. Follow the same algorithm for each node.
Insert() : insert new key into BST
Whenever an element is to be inserted, first locate its proper location. Start searching from the root node, then if the data is less than the key value, search for the empty location in the left subtree and insert the data. Otherwise, search for the empty location in the right subtree and insert the data.
•There are 3 cases which should be considered:
If the key is in a leaf, just delete that node
If the key is in a node which has one child, delete that node and connect its child to its parent
If the key is in a node which has two children, find the right most child of its left sub tree (node P), replace its key with P’s key and remove P recursively. (or alternately you can choose the left most child of its right sub tree)
If the key is in a leaf, just delete that node
If the key is in a node which has one child, delete that node and connect its child to its parent
If the key is in a node which has two children, find the right most child of its left sub tree (node P), replace its key with P’s key and remove P recursively. (or alternately you can choose the left most child of its right sub tree)
Source:
https://study.com/academy/lesson/linked-lists-in-c-programming-definition-example.html
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/circular-singly-linked-list-insertion/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/doubly-circular-linked-list-set-1-introduction-and-insertion/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hash_tablehttps://www.geeksforgeeks.org/circular-singly-linked-list-insertion/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/doubly-circular-linked-list-set-1-introduction-and-insertion/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/mid-square-hashing/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_tree


Comments
Post a Comment